Integrating IndoorGML with outdoors:Automatic routing graph generation for indoor‐outdoor transitional space for seamless navigation
Background:
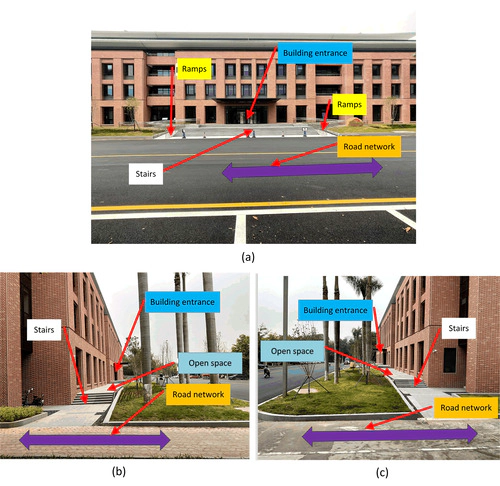
With the fast expansion of modern cities, the complexity of urban environments has significantly increased, creating a need for assistance for seamless indoor‐outdoor navigation. To meet this need, a number of standards and methods have emerged. Among them, IndoorGML is a well‐developed standard with the focus on indoor location‐based services. This standard has already been accepted by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and is now under active development. Although some mechanisms in IndoorGML have been defined to enable integration of indoor and outdoor networks, there are still no concrete guidelines for determination of indoor‐outdoor connections. It also lacks solid scientific foundations and efficient tools to extract the connecting nodes and edges that link indoor and outdoor spaces. To address this gap, in this scientific initiative we focus on connection of indoor and outdoor spaces and aim to provide a tool to automatically construct navigation graphs of the indoor‐outdoor transitional space to support seamless integration of indoor‐outdoor navigation. We expect that the developments from this project will benefit the IndoorGML ecosystem and greatly advance the capability of IndoorGML in representing navigable space and in supporting location-based services.
Objectives:
In this scientific initiative, we focus on modeling of indoor-outdoor transitional space, and aim to develop a tool which can automatically construct navigation graphs for indoor-outdoor transitional space to seamlessly link the outdoor and indoor enviroment. To this end, we will address the following two research objectives:
Research objective 1: Development of voxel models for indoor-outdoor transitional space. We will explore the use of voxel‐based modelling to capture the space between indoor and outdoor environments (e.g., parking slots, stairs, and sidewalks). Voxels will be enriched with semantics and segmented to distinguish between navigable space and non-navigable space.
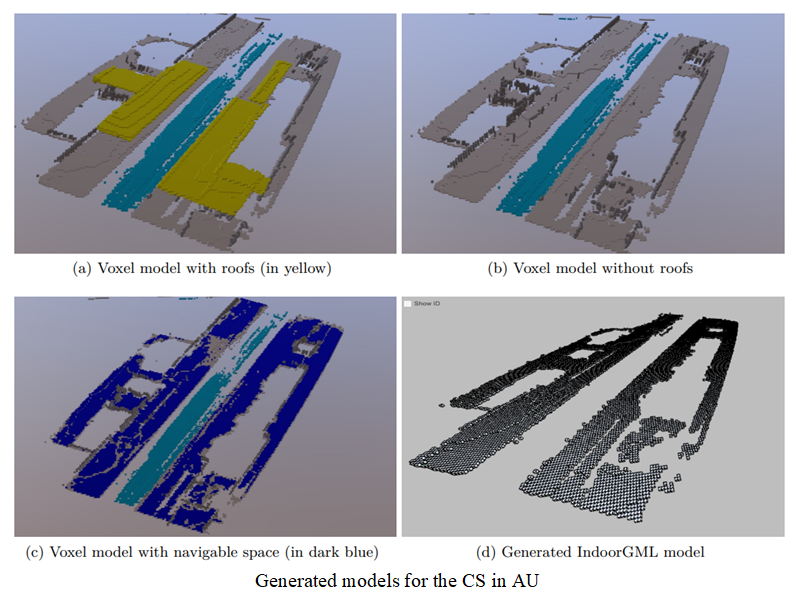
Research objective 2: Development of a tool for automatic routing graph generation for indoor-outdoor transitional space. The intended tool will: 1) generate voxel models from point clouds of building entrances and their surrounding environments; (2) identify navigable space and perform space division; 3) build navigation graphs that link the outdoor and indoor enviroment.
Result:
We have applied the developed python tool to the collected point cloud datasets and generated the voxel models as well as IndoorGML models. We have also tested the tool with some routing cases.For a detailed elaboration of the result, please refer to the main output of this project.
Main Output:
[1]A data repository containing the datasets used in this project, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.25323826
[2]A GitHub repository containing the source codes of the python tool developed from this project, https://github.com/tgis-lab/geopcd2indoorgml
Collaborating Team:
PI Zhiyong Wang (ISPRS WG IV/8), South China University of Technology, zwang1984@scut.edu.cn
Co-PI
Mir Abolfazl Mostafavi (ISPRS WG IV/8), Université Laval, Mir-Abolfazl.Mostafavi@scg.ulaval.ca
Kourosh Khoshelham (ISPRS ICWG II/Ib), University of Melbourne, k.khoshelham@unimelb.edu.au
Lucía Díaz Vilariño (ISPRS WG IV/9), Universidade de Vigo, lucia@uvigo.es
Sisi Zlatanova (ISPRS TC IV, OGC IndoorGML), UNSW, s.zlatanova@unsw.edu.au
Ki-Joune Li (OGC IndoorGML), Pusan National University, lik@pnu.edu
Related Publications:
Wang, Z., Zlatanova, S., Mostafavi, M. A., Khoshelham, K., Díaz-Vilariño, L., & Li, K. J. (2023). Automatic Generation of Routing Graphs for Indoor-Outdoor Transitional Space to Support Seamless Navigation. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 10, 487-492.
